Midterm Study Guide (2021-2022 School Year)
What is chemistry
the study of the properties and behavior of matter
What is matter
matter is any substance that has mass and takes up space by having volume.
Chemical vs. Physical Property
Physical Properties:
- Examples: Boiling point, Density, Mass, and Volume
Chemical Properties:
- Examples: Flammability, Corrosiveness, or Reactivity with acids
Chemical vs. Physical Change
Chemcial Change
-
not easily reversed
-
new products formed
-
reactants used up
-
often heat/light/sound/fizzing occurs
-
electricity maye formed
-
precipitate may form
Physical Change
- easily reversed
- no new sustance created
- often just a state change
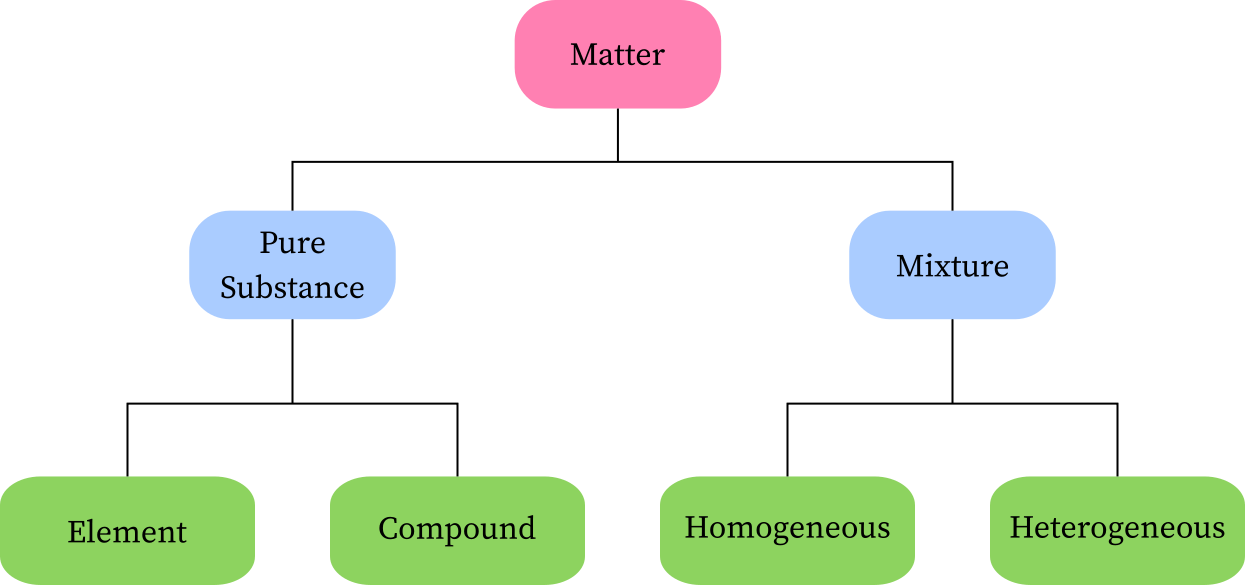
Pure Sustance vs. Mixture
There are two classfication under matter: mixture and substance.
Mixture: a combination of more than one substance
Substance: compound/element
Homogenous Mixture vs. Heterogenous Mixture
Homogenous: one that is mixed/dissolved together, like saltwater
Heterogenous: a mixture of two or more substances that are not soluble with each other, like sand and water
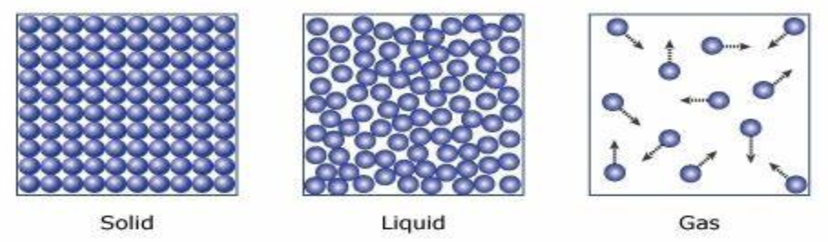
Three States of Matter
Intensive Property & Extensive Property
Intensive Property: a property that is a system of physical properties that does not depend on the size or amount of the system
- Examples: melting point, boiling point, etc.
Extensive Property: a property that totally depends on the size or amount of the material (varies with a change of volume/amount)
- Examples: weight, mass, volume, etc.
Unit Conversion
skip
Desity
Density = Mass / Volume
$$d=\frac mv$$
Atom
Atom: the smallest particle of a chemical element that can exist
Molecular Compound && Ionic Compound
Molecular Compound: is formed by the reaction of two or more nonmetals Ionic Compounds: formed by the reaction of a metal with a non-metal
Naming
Naming Ionic Compounds: Find the charge of the cation and make it equal to the anion charge (the roman numerals) and add the suffix -ide to the end of the 2nd element
$ Cu_2O$→Copper(1)Oxide
Terms
Ions
Cations: positively charged ions formed from neutral atoms (metal) (Left side on PT)
- Formed when an electron is lost
Anions: are the negatively charged ions formed from neutral atoms (nonmetal) (Right Side on PT)
- Formed when an electron is gained
Groups and Periods
Groups: *the vertical columns *(down) the table Periods: the horizontal rows (across) the periodic table
Specific names
Metals: located on the left side of the periodic table
Non-Metals: located on the right side of the periodic table (plus hydrogen)
Metalloids: located along the step formation on the right side of the periodic table
Alkali Metals: located along group 1
Alkaline Earth Metals: located along group 2
Halogens: located along group 17
Noble Gases: located along group 18 (the most stable elements and the least likely to react in a reaction)